The Role of Plankton as Indicators of Water Quality in Freshwater and Marine Ecosystems
By. Azizah - 01 Aug 2025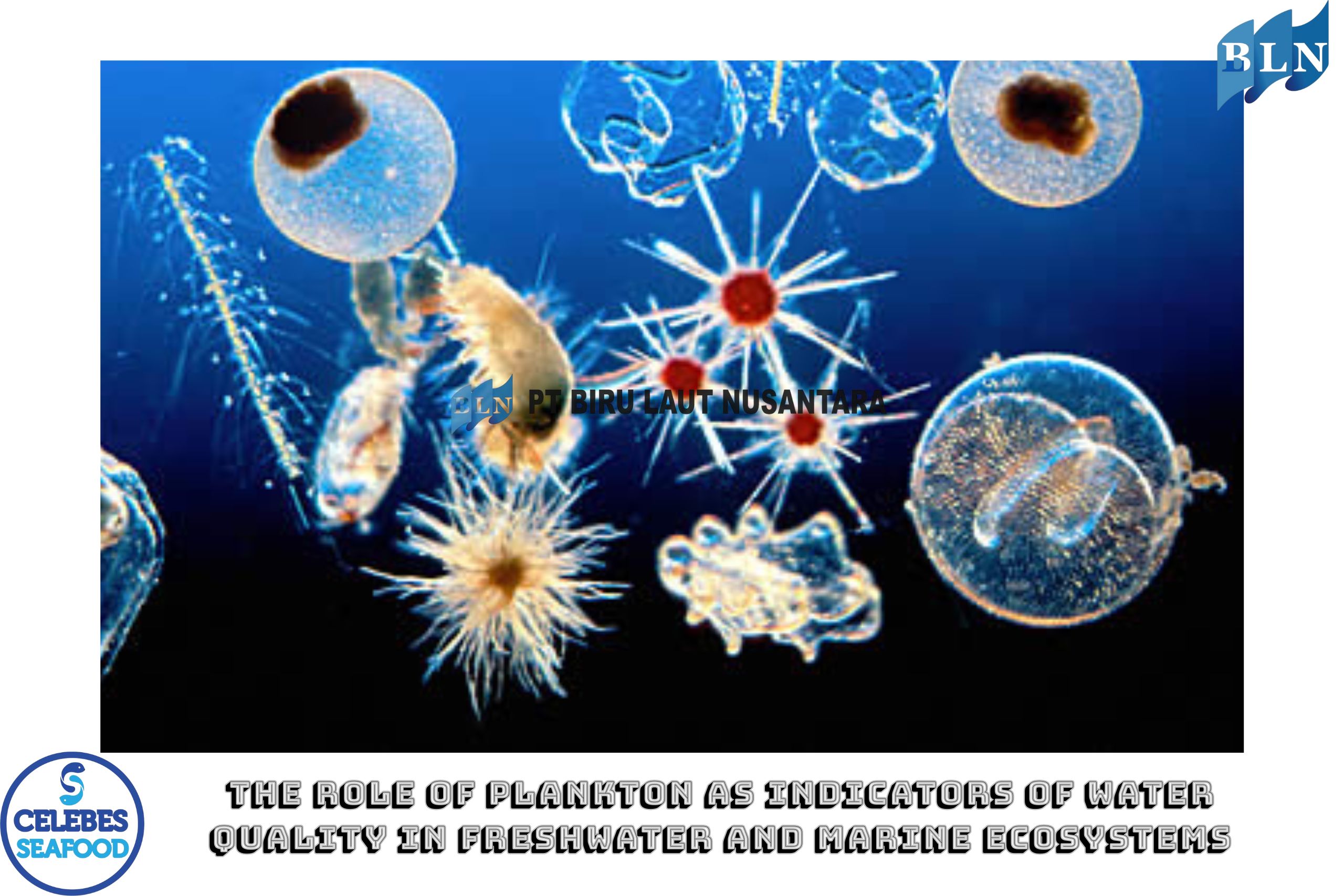
lautnusantara.comPlankton are microscopic organisms tplankton, biological indicators, water quality, phytoplankton, zooplankton, freshwater, marine watershat play a vital role in both freshwater and marine ecosystems. Their presence, composition, and abundance are highly sensitive to changes in water quality, making them natural bioindicators. This article reviews the role of phytoplankton and zooplankton in indicating trophic conditions, pollution impacts, and environmental dynamics. The study also compares the function of plankton in freshwater and marine ecosystems and explores their potential in sustainable environmental monitoring systems.
1. Introduction
Water quality is a crucial factor that determines the sustainability of aquatic ecosystems. Traditionally, water quality assessments rely on physical and chemical parameters, but biological approaches using plankton as indicators are increasingly adopted because they reflect long-term and cumulative environmental conditions. Plankton are generally classified into two major groups: phytoplankton (plant-like plankton) and zooplankton (animal-like plankton). Both groups are highly sensitive to environmental changes such as nutrient levels, temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen, and the presence of pollutants.
2. Characteristics of Plankton as Bioindicators
Plankton have short life cycles and respond quickly to changes in water quality. Phytoplankton serve as primary producers and are strongly influenced by light availability and nutrients such as nitrogen and phosphate. Zooplankton, which feed on phytoplankton, reflect the status of the food web and ecological balance. The dominance of certain species such as Microcystis (phytoplankton) or Brachionus (zooplankton) is often associated with eutrophication or organic pollution.
3. Comparison in Freshwater and Marine Waters
-
Freshwater Ecosystems: In lakes, rivers, and reservoirs, phytoplankton such as Chlorella, Scenedesmus, and Anabaena are often used as indicators of water quality. Eutrophication in freshwater bodies frequently leads to algal blooms, which reduce oxygen levels and harm other aquatic organisms.
-
Marine Ecosystems: In the ocean, plankton communities reflect salinity, currents, and marine pollution conditions. The presence of dinoflagellates and diatoms such as Ceratium and Thalassiosira indicate nutrient-rich or polluted marine waters.
4. Case Studies and Applications
Numerous studies have shown that plankton communities undergo significant changes in waters contaminated by domestic or industrial waste. In urban river waters, dominance by Euglena and Oscillatoria indicates high levels of organic pollution. In marine waters, the presence of Noctiluca scintillans is often associated with population blooms caused by nutrient influx from terrestrial runoff.
5. Potential and Challenges of Using Plankton as Indicators
Plankton provide a cost-effective and efficient means of monitoring water quality. However, their use requires accurate species identification and ecological interpretation. Key challenges include the need for taxonomic expertise and the natural variability of plankton communities across seasons and regions.
If you are interested in our Redfin Emperor Fillet Skin On,Robinson Sea Bream Fillet Skin On please do not hesitate to contact us through email and/or whatsapp.




 and Its Impact on Indonesia's Maritime Economy.jpg)

 in Marine Ecosystem Balanceks paragraf Anda.jpg)
