The Science Behind Ocean Currents and Their Effects
By. Nindi - 25 Mar 2025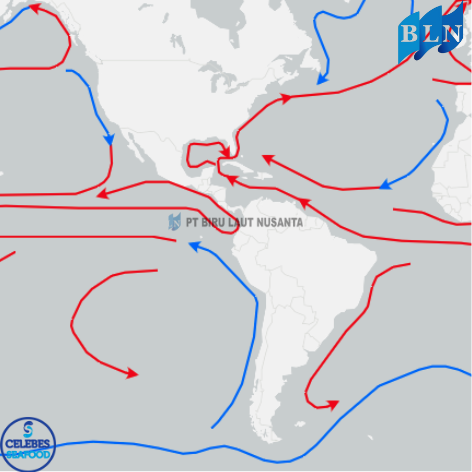
lautnusantara.com Ocean currents play a vital role in regulating the Earth's climate, supporting marine life, and influencing human activities such as navigation and fishing. These currents are driven by a combination of wind, temperature differences, salinity variations, and the Earth's rotation. Understanding how ocean currents work and their effects on the environment is crucial for predicting weather patterns, managing fisheries, and addressing climate change.
Causes of Ocean Currents
Ocean currents are generated by several natural forces, including:
-
Wind Patterns – Surface currents are primarily driven by global wind systems such as trade winds and westerlies.
-
Temperature and Salinity Differences – Variations in water density due to temperature and salinity differences create deep ocean currents in a process known as thermohaline circulation.
-
Coriolis Effect – The Earth's rotation causes moving water to deflect to the right in the Northern Hemisphere and to the left in the Southern Hemisphere.
-
Coastal and Tidal Effects – The shape of coastlines and the gravitational pull of the moon influence local currents and tides.
-
Upwelling and Downwelling – Vertical movements of water bring nutrients from the deep ocean to the surface, supporting marine ecosystems.
Effects of Ocean Currents
Ocean currents have a significant impact on the environment and human activities:
-
Climate Regulation – Currents distribute heat across the globe, influencing weather patterns and regional climates.
-
Marine Biodiversity – The movement of water transports nutrients and oxygen, sustaining marine ecosystems and fisheries.
-
Navigation and Trade – Historically, ocean currents have guided sailors and continue to influence modern shipping routes.
-
Fisheries and Food Supply – Upwelling currents bring nutrient-rich waters to the surface, supporting fish populations and global seafood industries.
-
Climate Change Impacts – Changes in ocean currents due to global warming can disrupt ecosystems, intensify storms, and affect sea level rise.
Possible Solutions and Adaptation
Understanding and monitoring ocean currents is essential for mitigating their potential negative impacts:
-
Scientific Research and Observation – Satellites, buoys, and oceanographic studies help track changes in ocean circulation.
-
Sustainable Fishing Practices – Managing fisheries based on ocean current patterns can prevent overfishing and protect marine biodiversity.
-
Climate Action Policies – Reducing carbon emissions can help slow climate change and its effects on ocean currents.
-
Disaster Preparedness – Coastal communities can use ocean current data to predict hurricanes, tsunamis, and rising sea levels.
Ocean currents are a fundamental force shaping the Earth's climate, marine ecosystems, and human activities. By understanding their science and effects, we can make informed decisions to protect the environment, sustain fisheries, and prepare for the challenges posed by climate change.






.jpg)

